How To Get The Range In Math
How to find the range of a data set
Published on September 11, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on September 25, 2020.
In statistics, the range is the spread of your data from the lowest to the highest value in the distribution. It is a commonly used measure of variability.
Along with measures of central tendency, measures of variability give you descriptive statistics for summarizing your data set.
The range is calculated by subtracting the lowest value from the highest value. While a large range means high variability, a small range means low variability in a distribution.
Calculate the range
The formula to calculate the range is:
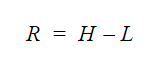
- R = range
- H = highest value
- L = lowest value
The range is the easiest measure of variability to calculate. To find the range, follow these steps:
- Order all values in your data set from low to high.
- Subtract the lowest value from the highest value.
This process is the same regardless of whether your values are positive or negative, or whole numbers or fractions.
| Participant | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 37 | 19 | 31 | 29 | 21 | 26 | 33 | 36 |
First, order the values from low to high to identify the lowest value (L) and thehighest value (H).
| Age | 19 | 21 | 26 | 29 | 31 | 33 | 36 | 37 |
|---|
Then subtract the lowest from the highest value.
R = H – L
R = 37 – 19 = 18
The range of our data set is 18 years.
How useful is the range?
The range generally gives you a good indicator of variability when you have a distribution without extreme values. When paired with measures of central tendency, the range can tell you about the span of the distribution.
But the range can be misleading when you have outliers in your data set. One extreme value in the data will give you a completely different range.
| Age | 19 | 21 | 26 | 29 | 31 | 33 | 36 | 61 |
|---|
Using the same calculation, we get a very different result this time:
R = H – L
R = 61 – 19 = 42
With an outlier, our range is now 42 years.
In the example above, the range indicates much more variability in the data than there actually is. Although we have a large range, most values are actually clustered around a clear middle.
Because only two numbers are used, the range is easily influenced by outliers. It can't tell you about the shape of the distribution of values on its own.
To get a clear idea of your data's variability, the range is best used in combination with other measures of variability like interquartile range and standard deviation.
Receive feedback on language, structure and layout
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Grammar
- Style consistency
See an example
Frequently asked questions about the range
Is this article helpful?
You have already voted. Thanks :-) Your vote is saved :-) Processing your vote...
How To Get The Range In Math
Source: https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/range/
Posted by: ruizresiduchathe.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Get The Range In Math"
Post a Comment